The World of Spices: From Bland to Hot
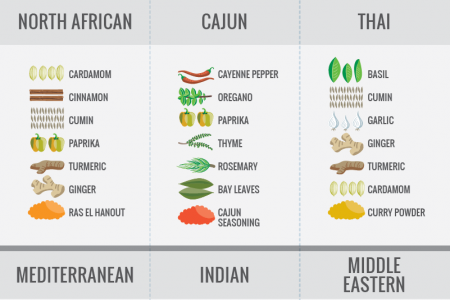
Common spice mixtures The Origin of Spices Origin • Clove Moluccas (Indonesia) • Cinnamon Sri Lanka, India, SE Asia • Pepper Hills of western India UK- Nutmeg Papua New Guinea, Moluccas (Indonesia) Mixed spice France Quatre épices Georgla Khmeli suneli * Vanilla Mexico USA Old Bay Seasoning Pumpkin pie spice North Africa Hartssa Ras el hanout Middle East |Za'atar -India Curry powder Pepper - Japan Shichimi togarasht China Five-spice powder - South Asta Garam masala Masala Clove Nutmeg Evolution Arab world & Middle East Baharat Ethiopia & Eritrea - Berbere Vanilla Chillies & Pepper Jamaica Cinnamon 30 Million Tonnes Jerk spice 1961-2009 25 America Chili powder |20 India and Pakistan Chaat masala India and Bangladesh | Panch phoron 15 http://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/syllabi/423/8-1Spices%200f%20the%20World.pdf THE WORLD OF SPICES From Bland to Hot! IChillies and peppers, green IChillies and peppers, dry 10 Humans have been using spices for thousands of years, and they have played a dramatic role in the development of World civilization. 1961 1970 1980 1990 2000 2009 http://faostat.fao.org/site/567/DesktopDefault.aspx?PagelD=567#ancor World Trade International trade in spices is estimated to be around 400,000 tons annually, at US $1.5 billion. World production Table World spice production Percent of World Trade for Important Spices With different climates in different parts of the country, India is the first producer of the world and produces a variety of spices. Production (Mt) 2000 Spice 1. Pepper 1. India 2,255,800 33% 2. China 584,871 2. Capsicum 22% 3. Indonesia 260,902 Seed spices 15% 4. Pakistan 208,328 5. Nigeria 146,500 4. Tree spices 14% 6. Bangladesh 144,000 5. Turmeric 8% 7. Viet Nam 123,752 6. Ginger 6% 8. Ethiopia 110,960 7. Cardamon 4% 10 9. Mexico 91,755 10. Others 104,500 8. Vanilla 2% 6. World 4,939,990 http://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/syllabi/423/8-1Spices%20of%20the%20World.pdf Source:www.foodmarketexchange.com/datacenter/product/herb/herb/detail/dc_pi_hs_herbo406.htm Spices are still cultivated mostly by hand and are cleaned, vashed, and sun-dried for five to ten days. Scoville scale Measurement of the spicy heat (or piquance) of a chili pepper. The number of Scoville heat units (SHU) indicates the amount of capsaicin* present. Hotness Scoville Units Examples 0w0 15,000,000–16,000,000 Pure capsaicin 8,600,000-9,100,000 Various capsaicinoids (e.g., homocapsaicin, homodihydrocapsaicin, nordihydrocapsaicin) 1,463,700 5,000,000-5,300,000 Law enforcement-grade pepper spray, FN 303 irritant ammunition 855,000–1,463,700 Naga Viper pepper, Infinity Chilli, Bhut Jolokia, Trinidad Scorpion Butch T pepper World's hottest chilli grown by Aussies 350,000-580,000 Red Savina habanero Pepper is the most important commercial spice: 100,000-350,000 Habanero, Scotch bonnet, Datil pepper, Rocoto, Madame Jeanette, Peruvian White Habanero, Jamaican pepper 50,000–100,000 Byadgi chilli, Bird's eye chili, Malagueta pepper, Chiltepin pepper, Piri piri, Pequin pepper 60% 30,000–50,000 Guntur chilli, Cayenne pepper, Ají pepper, Tabasco pepper, Cumari pepper (Capsicum Chinese), Chipotle 10,000–23,000 Serrano pepper, Peter pepper, Aleppo pepper 3,500-8,000 Espelette pepper, Jalapeño, Guajillo pepper, New Mexican varieties, abasco sauce of the total volume of the spice trade. 1,000–2,500 Anaheim pepper, Poblano pepper, Rocotillo pepper, Peppadew *Capsaicin is a chemical compound that stimulates chemoreceptor nerve endings in the skin, especially the mucous membranes. http://www.hawaii.edu/hga/GAW97/trade.html Timeline Spices were among the most valuable items of trade in ancient and medieval times. they were rare and precious products, used for medicine, perfume, incense, and flavoring and played a big role throughout human history. 3000 BC to 200 BC For thousands of years, Arab middlemen controlled the spice trade. 200 BC to 800 The Romans control the trade. 700 to 1500, the Republic of Venice had the monopoly on spice trade with the Middle East 2011: International trade: over US$1.5 billion per year. 3000 BC O AD 2000 BC The Old Testament includes much about herbs 1000 BC 1000 BC medical systems based upon herbs could be found in China, Korea, and India. 2000 BC 3500 BC the ancient Egyptians were using various spices for flavouring food, in cosmetics, and for embalming their dead. 12th to 16th Century 1600 to 1900 Americans enter Europeans explore passages to the East Indies. the spice trade. In 1492; Christopher Columbus went westwards from Europe to find a sea route to the lands of spices but found the Americas. 15th to 17th Century Wars for control of the spice trade break out. 1500 to 1800 http://leslie-bilderback. suite 101.com/a-short-history-of-spices-091520 http://www.spiceadvice.com/history/index.html http://www.thespicetrader.co.nz/history-of-spice English exploration prepared by: O recipefinder The smart way to find recipes
The World of Spices: From Bland to Hot
Publisher
Recipe FinderSource
Unknown. Add a sourceCategory
FoodGet a Quote