The Evolution of Ram & Processors
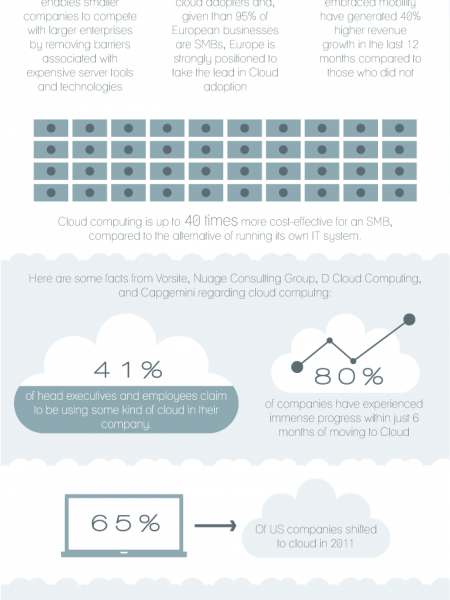
The Evolution Of RAM PROCESSORS RAM 1966-2030 23 YEAR GENERATION CHIP COST RAMSIZE COST OF 1 GIG OF RAM 1966 -4 $512 1 bit $512,000,000,000.00 1967 -3 4 bit $256,000,000,000.00 1968 16 bit $64,000,000,000.00 1969 -1 $256 64 bit $8,000,000,000.00 1970 256 bit $2,000,000,000.00 KILOBIT 1973 $128 1 Kilobit $256,000,0000.00 1976 4 kilobit $128,000,000.00 1979 16 kilobit $32,000,000.00 1982 4 $64 64 kilobit $4,000,000.00 1985 256 kilobit $1,000,000.00 MEGABIT 1988 $32 1 Megabit $128,000.000 1991 7 4 Megabit $64,000.00 1994 8 16 Megabit $16,000.00 1997 9 $16 64 Megabit $2,000.00 2000 10 256 Megabit $500.00 GIGABIT 2003 11 $8 1 Gigabit $64.00 2006 12 4 Gigabit $32.00 2009 13 16 Gigabit $8.00 2012 14 $4 64 Gigabit $1.00 2015 15 256 Gigabit $0.25 PETABIT 2018 1 Petabit 4 Petabit 16 $2 $0.03 2021 17 $0.02 2024 18 16 Petabit $0.004 2027 19 $1 64 Petabit $0.0005 2030 20 256 Petabit $0.0001 * ALTAIR 8800 CONPUTER PROCESSORS 1971-2013 1971 - INTEL 4004 • Designed by Federico Faggin and Ted Hoff of Intel and Masatoshi Shima INS832 of Busicom • 2,300 transistors • PMOS technology 0.092 Million Instructions Per Second 2,300 Transistors 1972 - INTEL 801 C8008 907OR • Developed by Victor Poor and Harry Pyle of CTC, and Ted Hoff, Faggin, Stanley Mazor and Hal Feeney of Intel • 3,500 transistors • clock speed of 0.5 MH 0,1 Million Instructions Per Second 3,500 Transistors 1974 - INTEL 8080 • Created by Faggin, Mazor and Masatoshi Shima • 6,000 transistors • Clock speed of 2 MHz. 0.29 Million Instructions Per Second 6,000 Transistors 1977 - INTEL 8085 • Also used as a microcontroller Worked on +5V supply It was also the first time that the von • Neumann architecture was used 0.5 Million Instructions Per Second 6,500 Transistors 1979 - INTEL 8088 • Based on the new HMOS technology 40-pin DIP as well as PLCC package. • The data path was only 8-bit • Clock speed was 10 MHz. 1 Million Instructions Per Second 29,000 Transistors 1985 - INTEL 80386 intel 1386 • 32-bit microprocessor • Clock speed up to 40 MHz • Had 275,000 transistors • Also known as the i386 II 5 Million Instructions Per Second 275,000 Transistors 1989 - INTEL 80486 • The first tightly pipelined x86 design • First x86 chip to use more than a million transistors • Integrated FPU with a dedicated local bus 20 Million Instructions Per Second 1.2 Million Translstors 1993 – Pentium Processor • Started with the launch of the P5 processor • Came in two models - 510-pin version with 60 MHz clock intel. pentium- speed and 567-pin version with • It had 3.1 million transistors • 32-bit processor clock speed of 66 MHz. 48.2 Million Instructions Per Second 3.1 Million Translstors 1995 – Pentium Pro • First processor of the Pentium II series • Clock speed of 200 MHz • Built to run in quad as well as dual processor configurations. • 5.5 million transistors intel. PENTIUM PRO 161 Million Instructions Per Second 5.5 Million Translstors 1997 - Pentium II Music • Pentium II family had a vast range of processors to offer. • Clock speed was increased gradually with every model launched to up to 450 MHz. pentumil 368 Million Instructions Per Second 7.5 Million Translstors 1999 - Pentium III • SSE instruction that accelerated the floating point calculations • Models offered up to 1.4 GHz clock speed • 9.5 million transistors 816 Million Instructions Per Second 28.1 Million Translstors 2000 – Pentium ID intel. pentium 4 New single core processor family • Achieved a clock speed between 1.3 GHz to 3.08 GHz. 1342 Million Instructions Per Second 42 Million Transistors 2003 - Pentium M • This processor was a mobile single-core processor from Intel. • Clock speed of 2.26 GHz. intel. 1538 Million Instructions Per Second 77 Million Transistors 2006 - Core 2 (intel • Also known as E6320 • Clock speed capable of achieving up to 3.5 GHz • Processors launched under this family were single-core, dual-core and quad-core. Core 2 Duo 1557 Million Instructions Per Second 291 Million Translstors TODAY Sandy Bridge (Core 13, 15, 17) (intei) • Intel Quick sync for video encoding & decoding • Improved 256-bit/cycle ring bus connect • Clock speeds can reach up to 3.8 GHz • Transistor count reaches up to 2.27 billion. Sandy Bridge 3004 Million Instructions Per Second 624 Million Translstors Ivy Bridge (Core 13, 15, 17) (intel) • 22-nm die processor • Reduced die is possible due to the use of the 3D (tri-gate) transistors • 3D transistors reduce the power consumption to almost 50% less than the 2D ones Ivy Bridge • Includes special support for PCI Express • Better graphics with DirectX 11 • Clock speed is about 3.80 GHz. • 20°C higher temperature than Sandy Bridge. 10000 Million Instructions Per Second 1.4 Billion Transistors Processor metrics listed above are general estimates. Actually processor performance metrics and configurations may vary based on the processor model and testing conditions. Sources: http://www.archivebuilders.com/whitepapers/22045p.pdf http://www.buzzle.com/articles/history-of-computer-processors.html http://www.ehow.com/facts_6067219_evolution-computer-processor.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Intel_microprocessors#intel_4004 http://parallelis.com/x86-code-on-intel-xeon-phi/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Instructions_per_second http://www.roylongbottom.org.uk/whetstone%20results.htm Brought to you by Chassis Plans CHASSIS PLANS Systems Engineered to Perform %24 The Evolution Of RAM PROCESSORS RAM 1966-2030 23 YEAR GENERATION CHIP COST RAMSIZE COST OF 1 GIG OF RAM 1966 -4 $512 1 bit $512,000,000,000.00 1967 -3 4 bit $256,000,000,000.00 1968 16 bit $64,000,000,000.00 1969 -1 $256 64 bit $8,000,000,000.00 1970 256 bit $2,000,000,000.00 KILOBIT 1973 $128 1 Kilobit $256,000,0000.00 1976 4 kilobit $128,000,000.00 1979 16 kilobit $32,000,000.00 1982 4 $64 64 kilobit $4,000,000.00 1985 256 kilobit $1,000,000.00 MEGABIT 1988 $32 1 Megabit $128,000.000 1991 7 4 Megabit $64,000.00 1994 8 16 Megabit $16,000.00 1997 9 $16 64 Megabit $2,000.00 2000 10 256 Megabit $500.00 GIGABIT 2003 11 $8 1 Gigabit $64.00 2006 12 4 Gigabit $32.00 2009 13 16 Gigabit $8.00 2012 14 $4 64 Gigabit $1.00 2015 15 256 Gigabit $0.25 PETABIT 2018 1 Petabit 4 Petabit 16 $2 $0.03 2021 17 $0.02 2024 18 16 Petabit $0.004 2027 19 $1 64 Petabit $0.0005 2030 20 256 Petabit $0.0001 * ALTAIR 8800 CONPUTER PROCESSORS 1971-2013 1971 - INTEL 4004 • Designed by Federico Faggin and Ted Hoff of Intel and Masatoshi Shima INS832 of Busicom • 2,300 transistors • PMOS technology 0.092 Million Instructions Per Second 2,300 Transistors 1972 - INTEL 801 C8008 907OR • Developed by Victor Poor and Harry Pyle of CTC, and Ted Hoff, Faggin, Stanley Mazor and Hal Feeney of Intel • 3,500 transistors • clock speed of 0.5 MH 0,1 Million Instructions Per Second 3,500 Transistors 1974 - INTEL 8080 • Created by Faggin, Mazor and Masatoshi Shima • 6,000 transistors • Clock speed of 2 MHz. 0.29 Million Instructions Per Second 6,000 Transistors 1977 - INTEL 8085 • Also used as a microcontroller Worked on +5V supply It was also the first time that the von • Neumann architecture was used 0.5 Million Instructions Per Second 6,500 Transistors 1979 - INTEL 8088 • Based on the new HMOS technology 40-pin DIP as well as PLCC package. • The data path was only 8-bit • Clock speed was 10 MHz. 1 Million Instructions Per Second 29,000 Transistors 1985 - INTEL 80386 intel 1386 • 32-bit microprocessor • Clock speed up to 40 MHz • Had 275,000 transistors • Also known as the i386 II 5 Million Instructions Per Second 275,000 Transistors 1989 - INTEL 80486 • The first tightly pipelined x86 design • First x86 chip to use more than a million transistors • Integrated FPU with a dedicated local bus 20 Million Instructions Per Second 1.2 Million Translstors 1993 – Pentium Processor • Started with the launch of the P5 processor • Came in two models - 510-pin version with 60 MHz clock intel. pentium- speed and 567-pin version with • It had 3.1 million transistors • 32-bit processor clock speed of 66 MHz. 48.2 Million Instructions Per Second 3.1 Million Translstors 1995 – Pentium Pro • First processor of the Pentium II series • Clock speed of 200 MHz • Built to run in quad as well as dual processor configurations. • 5.5 million transistors intel. PENTIUM PRO 161 Million Instructions Per Second 5.5 Million Translstors 1997 - Pentium II Music • Pentium II family had a vast range of processors to offer. • Clock speed was increased gradually with every model launched to up to 450 MHz. pentumil 368 Million Instructions Per Second 7.5 Million Translstors 1999 - Pentium III • SSE instruction that accelerated the floating point calculations • Models offered up to 1.4 GHz clock speed • 9.5 million transistors 816 Million Instructions Per Second 28.1 Million Translstors 2000 – Pentium ID intel. pentium 4 New single core processor family • Achieved a clock speed between 1.3 GHz to 3.08 GHz. 1342 Million Instructions Per Second 42 Million Transistors 2003 - Pentium M • This processor was a mobile single-core processor from Intel. • Clock speed of 2.26 GHz. intel. 1538 Million Instructions Per Second 77 Million Transistors 2006 - Core 2 (intel • Also known as E6320 • Clock speed capable of achieving up to 3.5 GHz • Processors launched under this family were single-core, dual-core and quad-core. Core 2 Duo 1557 Million Instructions Per Second 291 Million Translstors TODAY Sandy Bridge (Core 13, 15, 17) (intei) • Intel Quick sync for video encoding & decoding • Improved 256-bit/cycle ring bus connect • Clock speeds can reach up to 3.8 GHz • Transistor count reaches up to 2.27 billion. Sandy Bridge 3004 Million Instructions Per Second 624 Million Translstors Ivy Bridge (Core 13, 15, 17) (intel) • 22-nm die processor • Reduced die is possible due to the use of the 3D (tri-gate) transistors • 3D transistors reduce the power consumption to almost 50% less than the 2D ones Ivy Bridge • Includes special support for PCI Express • Better graphics with DirectX 11 • Clock speed is about 3.80 GHz. • 20°C higher temperature than Sandy Bridge. 10000 Million Instructions Per Second 1.4 Billion Transistors Processor metrics listed above are general estimates. Actually processor performance metrics and configurations may vary based on the processor model and testing conditions. Sources: http://www.archivebuilders.com/whitepapers/22045p.pdf http://www.buzzle.com/articles/history-of-computer-processors.html http://www.ehow.com/facts_6067219_evolution-computer-processor.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Intel_microprocessors#intel_4004 http://parallelis.com/x86-code-on-intel-xeon-phi/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Instructions_per_second http://www.roylongbottom.org.uk/whetstone%20results.htm Brought to you by Chassis Plans CHASSIS PLANS Systems Engineered to Perform %24
The Evolution of Ram & Processors
Source
http://www.c...sis-plans/Category
ComputersGet a Quote