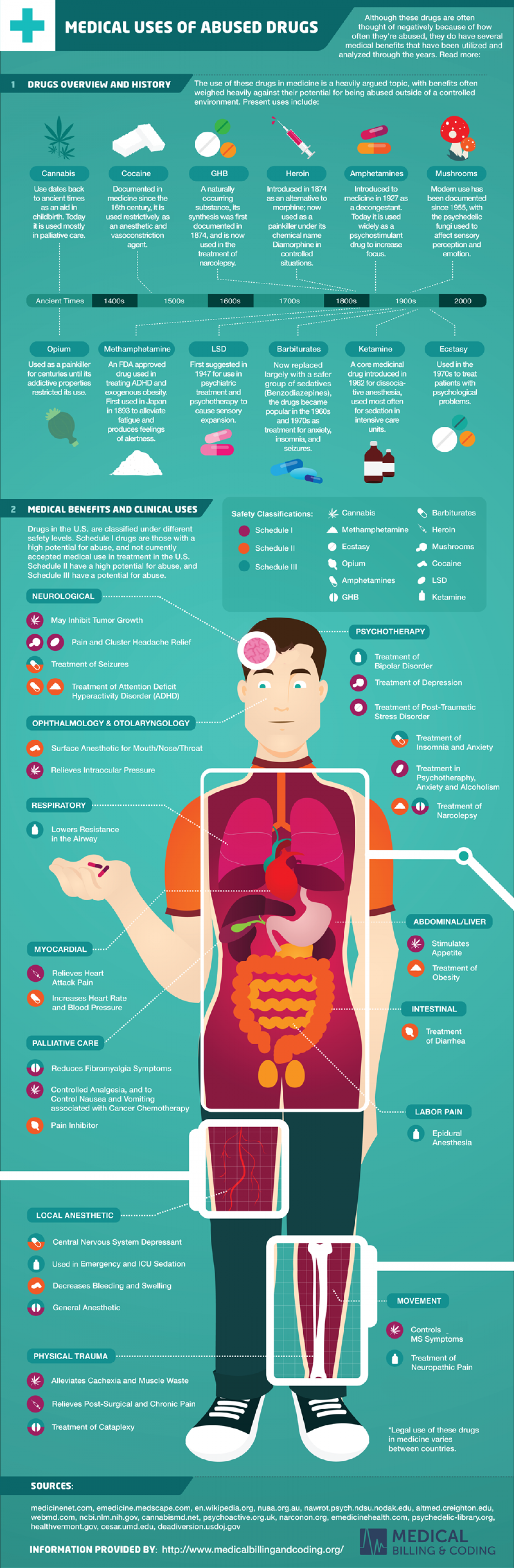
Medical Uses Of Abused Drugs
Although these drugs are often thought of negatively because of how often they're abused, they do have several medical benefits that have been utilized and MEDICAL USES OF ABUSED DRUGS analyzed through the years. Read more: The use of these drugs in medicine is a heavily argued topic, with benefits often weighed heavily against their potential for being abused outside of a controlled environment. Present uses include: 1 DRUGS OVERVIEW AND HISTORY Cannabis Cocaine GHB Heroin Amphetamines Mushrooms Documented in medicine since the 16th century, it is used restrictively as A naturally occumring substance, its synthesis was first documented in Use dates back Introduced in 1874 Introduced to Modem use has been documented since 1955, with the psychedelic fungi used to affect sensory perception and emotion. to ancient times as an altemative to medicine in 1927 as morphine; now used as a painkiller under its chemical name a decongestant. Today it is used as an aid in childbirth. Today it is used mostly in palliative care. an anesthetic and widely as a psychostimulant drug to increase vasoconstriction 1874, and is now agent. used in the Diamorphine in controlled treatment of focus. narcolepsy. situations. Ancient Times 1400s 1500s 1600s 1700s 1800s 1900s 2000 Opium Methamphetamine LSD Barbiturates Ketamine Ecstasy A core medicinal drug introduced in 1962 for dissocia- tive anesthesia, used most often An FDA approved Used as a painkiller for centuries until its addictive properties First suggested in 1947 for use in Now replaced largely with a safer group of sedatives (Benzodiazepines), the drugs became popular in the 1960s and 1970s as treatment for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Used in the 1970s to treat patients with psychological problems. drug used in treating ADHD and exogenous obesity. First used in Japan in 1893 to alleviate fatigue and produces feelings of alertness. psychiatric treatment and restricted its use. psychotherapy to for sedation in intensive care cause sensory expansion. units. MEDICAL BENEFITS AND CLINICAL USES Safety Classifications: K Cannabis S Barbiturates Drugs in the U.S. are classified under different safety levels. Schedule I drugs are those with a high potential for abuse, and not currently accepted medical use in treatment in the U.S. Schedule II have a high potential for abuse, and Schedule III have a potential for abuse. Schedule I Methamphetamine Heroin Schedule II Ecstasy Mushrooms Schedule III Opium Cocaine A Amphetamines LSD NEUROLOGICAL O GHB Ketamine May Inhibit Tumor Growth PSYCHOTHERAPY Pain and Cluster Headache Relief Treatment of Treatment of Seizures Bipolar Disorder Treatment of Depression Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder OPHTHALMOLOGY & OTOLARYNGOLOGY Treatment of Surface Anesthetic for Mouth/Nose/Throat Insomnia and Anxiety Relieves Intraocular Pressure Treatment in Psychotheraphy, Anxiety and Alcoholism RESPIRATORY Treatment of Narcolepsy Lowers Resistance in the Airway .... .... ABDOMINAL/LIVER V Stimulates MYOCARDIAL Appetite Treatment of Obesity Relieves Heart Attack Pain Increases Heart Rate and Blood Pressure INTESTINAL Treatment of Diarrhea PALLIATIVE CARE Reduces Fibromyalgia Symptoms A Controlled Analgesia, and to Control Nausea and Vomiting associated with Cancer Chemotherapy LABOR PAIN Pain Inhibitor Epidural Anesthesia LOCAL ANESTHETIC Central Nervous System Depressant Used in Emergency and ICU Sedation Decreases Bleeding and Swelling MOVEMENT General Anesthetic K Controls MS Symptoms PHYSICAL TRAUMA Treatment of Neuropathic Pain Alleviates Cachexia and Muscle Waste Relieves Post-Surgical and Chronic Pain Treatment of Cataplexy *Legal use of these drugs in medicine varies between countries. SOURCES: medicinenet.com, emedicine.medscape.com, en.wikipedia.org, nuaa.org.au, nawrot.psych.ndsu.nodak.edu, altmed.creighton.edu, webmd.com, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, cannabismd.net, psychoactive.org.uk, narconon.org, emedicinehealth.com, psychedelic-library.org, healthvermont.gov, cesar.umd.edu, deadiversion.usdoj.gov MEDICAL INFORMATION PROVIDED BY: http://www.medicalbillingandcoding.org/ BILLING & CODING Although these drugs are often thought of negatively because of how often they're abused, they do have several medical benefits that have been utilized and MEDICAL USES OF ABUSED DRUGS analyzed through the years. Read more: The use of these drugs in medicine is a heavily argued topic, with benefits often weighed heavily against their potential for being abused outside of a controlled environment. Present uses include: 1 DRUGS OVERVIEW AND HISTORY Cannabis Cocaine GHB Heroin Amphetamines Mushrooms Documented in medicine since the 16th century, it is used restrictively as A naturally occumring substance, its synthesis was first documented in Use dates back Introduced in 1874 Introduced to Modem use has been documented since 1955, with the psychedelic fungi used to affect sensory perception and emotion. to ancient times as an altemative to medicine in 1927 as morphine; now used as a painkiller under its chemical name a decongestant. Today it is used as an aid in childbirth. Today it is used mostly in palliative care. an anesthetic and widely as a psychostimulant drug to increase vasoconstriction 1874, and is now agent. used in the Diamorphine in controlled treatment of focus. narcolepsy. situations. Ancient Times 1400s 1500s 1600s 1700s 1800s 1900s 2000 Opium Methamphetamine LSD Barbiturates Ketamine Ecstasy A core medicinal drug introduced in 1962 for dissocia- tive anesthesia, used most often An FDA approved Used as a painkiller for centuries until its addictive properties First suggested in 1947 for use in Now replaced largely with a safer group of sedatives (Benzodiazepines), the drugs became popular in the 1960s and 1970s as treatment for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Used in the 1970s to treat patients with psychological problems. drug used in treating ADHD and exogenous obesity. First used in Japan in 1893 to alleviate fatigue and produces feelings of alertness. psychiatric treatment and restricted its use. psychotherapy to for sedation in intensive care cause sensory expansion. units. 2 MEDICAL BENEFITS AND CLINICAL USES Safety Classifications: K Cannabis S Barbiturates Drugs in the U.S. are classified under different safety levels. Schedule I drugs are those with a high potential for abuse, and not currently accepted medical use in treatment in the U.S. Schedule II have a high potential for abuse, and Schedule III have a potential for abuse. Schedule I Methamphetamine Heroin Schedule II Ecstasy Mushrooms Schedule III Opium Cocaine A Amphetamines LSD NEUROLOGICAL O GHB Ketamine May Inhibit Tumor Growth PSYCHOTHERAPY Pain and Cluster Headache Relief Treatment of Treatment of Seizures Bipolar Disorder Treatment of Depression Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder OPHTHALMOLOGY & OTOLARYNGOLOGY Treatment of Surface Anesthetic for Mouth/Nose/Throat Insomnia and Anxiety 米 Relieves Intraocular Pressure Treatment in Psychotheraphy, Anxiety and Alcoholism RESPIRATORY Treatment of Narcolepsy Lowers Resistance in the Airway .... .... ABDOMINAL/LIVER V Stimulates MYOCARDIAL Appetite Treatment of Obesity Relieves Heart Attack Pain Increases Heart Rate and Blood Pressure INTESTINAL Treatment of Diarrhea PALLIATIVE CARE Reduces Fibromyalgia Symptoms A Controlled Analgesia, and to Control Nausea and Vomiting associated with Cancer Chemotherapy LABOR PAIN Pain Inhibitor Epidural Anesthesia LOCAL ANESTHETIC Central Nervous System Depressant Used in Emergency and ICU Sedation Decreases Bleeding and Swelling MOVEMENT General Anesthetic K Controls MS Symptoms PHYSICAL TRAUMA Treatment of Neuropathic Pain Alleviates Cachexia and Muscle Waste Relieves Post-Surgical and Chronic Pain Treatment of Cataplexy *Legal use of these drugs in medicine varies between countries. SOURCES: medicinenet.com, emedicine.medscape.com, en.wikipedia.org, nuaa.org.au, nawrot.psych.ndsu.nodak.edu, altmed.creighton.edu, webmd.com, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, cannabismd.net, psychoactive.org.uk, narconon.org, emedicinehealth.com, psychedelic-library.org, healthvermont.gov, cesar.umd.edu, deadiversion.usdoj.gov MEDICAL INFORMATION PROVIDED BY: http://www.medicalbillingandcoding.org/ BILLING & CODING Although these drugs are often thought of negatively because of how often they're abused, they do have several medical benefits that have been utilized and MEDICAL USES OF ABUSED DRUGS analyzed through the years. Read more: The use of these drugs in medicine is a heavily argued topic, with benefits often weighed heavily against their potential for being abused outside of a controlled environment. Present uses include: 1 DRUGS OVERVIEW AND HISTORY Cannabis Cocaine GHB Heroin Amphetamines Mushrooms Documented in medicine since the 16th century, it is used restrictively as A naturally occumring substance, its synthesis was first documented in Use dates back Introduced in 1874 Introduced to Modem use has been documented since 1955, with the psychedelic fungi used to affect sensory perception and emotion. to ancient times as an altemative to medicine in 1927 as morphine; now used as a painkiller under its chemical name a decongestant. Today it is used as an aid in childbirth. Today it is used mostly in palliative care. an anesthetic and widely as a psychostimulant drug to increase vasoconstriction 1874, and is now agent. used in the Diamorphine in controlled treatment of focus. narcolepsy. situations. Ancient Times 1400s 1500s 1600s 1700s 1800s 1900s 2000 Opium Methamphetamine LSD Barbiturates Ketamine Ecstasy A core medicinal drug introduced in 1962 for dissocia- tive anesthesia, used most often An FDA approved Used as a painkiller for centuries until its addictive properties First suggested in 1947 for use in Now replaced largely with a safer group of sedatives (Benzodiazepines), the drugs became popular in the 1960s and 1970s as treatment for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Used in the 1970s to treat patients with psychological problems. drug used in treating ADHD and exogenous obesity. First used in Japan in 1893 to alleviate fatigue and produces feelings of alertness. psychiatric treatment and restricted its use. psychotherapy to for sedation in intensive care cause sensory expansion. units. 2 MEDICAL BENEFITS AND CLINICAL USES Safety Classifications: K Cannabis S Barbiturates Drugs in the U.S. are classified under different safety levels. Schedule I drugs are those with a high potential for abuse, and not currently accepted medical use in treatment in the U.S. Schedule II have a high potential for abuse, and Schedule III have a potential for abuse. Schedule I Methamphetamine Heroin Schedule II Ecstasy Mushrooms Schedule III Opium Cocaine A Amphetamines LSD NEUROLOGICAL O GHB Ketamine May Inhibit Tumor Growth PSYCHOTHERAPY Pain and Cluster Headache Relief Treatment of Treatment of Seizures Bipolar Disorder Treatment of Depression Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder OPHTHALMOLOGY & OTOLARYNGOLOGY Treatment of Surface Anesthetic for Mouth/Nose/Throat Insomnia and Anxiety 米 Relieves Intraocular Pressure Treatment in Psychotheraphy, Anxiety and Alcoholism RESPIRATORY Treatment of Narcolepsy Lowers Resistance in the Airway .... .... ABDOMINAL/LIVER V Stimulates MYOCARDIAL Appetite Treatment of Obesity Relieves Heart Attack Pain Increases Heart Rate and Blood Pressure INTESTINAL Treatment of Diarrhea PALLIATIVE CARE Reduces Fibromyalgia Symptoms A Controlled Analgesia, and to Control Nausea and Vomiting associated with Cancer Chemotherapy LABOR PAIN Pain Inhibitor Epidural Anesthesia LOCAL ANESTHETIC Central Nervous System Depressant Used in Emergency and ICU Sedation Decreases Bleeding and Swelling MOVEMENT General Anesthetic K Controls MS Symptoms PHYSICAL TRAUMA Treatment of Neuropathic Pain Alleviates Cachexia and Muscle Waste Relieves Post-Surgical and Chronic Pain Treatment of Cataplexy *Legal use of these drugs in medicine varies between countries. SOURCES: medicinenet.com, emedicine.medscape.com, en.wikipedia.org, nuaa.org.au, nawrot.psych.ndsu.nodak.edu, altmed.creighton.edu, webmd.com, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, cannabismd.net, psychoactive.org.uk, narconon.org, emedicinehealth.com, psychedelic-library.org, healthvermont.gov, cesar.umd.edu, deadiversion.usdoj.gov MEDICAL INFORMATION PROVIDED BY: http://www.medicalbillingandcoding.org/ BILLING & CODING Although these drugs are often thought of negatively because of how often they're abused, they do have several medical benefits that have been utilized and MEDICAL USES OF ABUSED DRUGS analyzed through the years. Read more: The use of these drugs in medicine is a heavily argued topic, with benefits often weighed heavily against their potential for being abused outside of a controlled environment. Present uses include: 1 DRUGS OVERVIEW AND HISTORY Cannabis Cocaine GHB Heroin Amphetamines Mushrooms Documented in medicine since the 16th century, it is used restrictively as A naturally occumring substance, its synthesis was first documented in Use dates back Introduced in 1874 Introduced to Modem use has been documented since 1955, with the psychedelic fungi used to affect sensory perception and emotion. to ancient times as an altemative to medicine in 1927 as morphine; now used as a painkiller under its chemical name a decongestant. Today it is used as an aid in childbirth. Today it is used mostly in palliative care. an anesthetic and widely as a psychostimulant drug to increase vasoconstriction 1874, and is now agent. used in the Diamorphine in controlled treatment of focus. narcolepsy. situations. Ancient Times 1400s 1500s 1600s 1700s 1800s 1900s 2000 Opium Methamphetamine LSD Barbiturates Ketamine Ecstasy A core medicinal drug introduced in 1962 for dissocia- tive anesthesia, used most often An FDA approved Used as a painkiller for centuries until its addictive properties First suggested in 1947 for use in Now replaced largely with a safer group of sedatives (Benzodiazepines), the drugs became popular in the 1960s and 1970s as treatment for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Used in the 1970s to treat patients with psychological problems. drug used in treating ADHD and exogenous obesity. First used in Japan in 1893 to alleviate fatigue and produces feelings of alertness. psychiatric treatment and restricted its use. psychotherapy to for sedation in intensive care cause sensory expansion. units. 2 MEDICAL BENEFITS AND CLINICAL USES Safety Classifications: K Cannabis S Barbiturates Drugs in the U.S. are classified under different safety levels. Schedule I drugs are those with a high potential for abuse, and not currently accepted medical use in treatment in the U.S. Schedule II have a high potential for abuse, and Schedule III have a potential for abuse. Schedule I Methamphetamine Heroin Schedule II Ecstasy Mushrooms Schedule III Opium Cocaine A Amphetamines LSD NEUROLOGICAL O GHB Ketamine May Inhibit Tumor Growth PSYCHOTHERAPY Pain and Cluster Headache Relief Treatment of Treatment of Seizures Bipolar Disorder Treatment of Depression Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder OPHTHALMOLOGY & OTOLARYNGOLOGY Treatment of Surface Anesthetic for Mouth/Nose/Throat Insomnia and Anxiety 米 Relieves Intraocular Pressure Treatment in Psychotheraphy, Anxiety and Alcoholism RESPIRATORY Treatment of Narcolepsy Lowers Resistance in the Airway .... .... ABDOMINAL/LIVER V Stimulates MYOCARDIAL Appetite Treatment of Obesity Relieves Heart Attack Pain Increases Heart Rate and Blood Pressure INTESTINAL Treatment of Diarrhea PALLIATIVE CARE Reduces Fibromyalgia Symptoms A Controlled Analgesia, and to Control Nausea and Vomiting associated with Cancer Chemotherapy LABOR PAIN Pain Inhibitor Epidural Anesthesia LOCAL ANESTHETIC Central Nervous System Depressant Used in Emergency and ICU Sedation Decreases Bleeding and Swelling MOVEMENT General Anesthetic K Controls MS Symptoms PHYSICAL TRAUMA Treatment of Neuropathic Pain Alleviates Cachexia and Muscle Waste Relieves Post-Surgical and Chronic Pain Treatment of Cataplexy *Legal use of these drugs in medicine varies between countries. SOURCES: medicinenet.com, emedicine.medscape.com, en.wikipedia.org, nuaa.org.au, nawrot.psych.ndsu.nodak.edu, altmed.creighton.edu, webmd.com, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, cannabismd.net, psychoactive.org.uk, narconon.org, emedicinehealth.com, psychedelic-library.org, healthvermont.gov, cesar.umd.edu, deadiversion.usdoj.gov MEDICAL INFORMATION PROVIDED BY: http://www.medicalbillingandcoding.org/ BILLING & CODING Although these drugs are often thought of negatively because of how often they're abused, they do have several medical benefits that have been utilized and MEDICAL USES OF ABUSED DRUGS analyzed through the years. Read more: The use of these drugs in medicine is a heavily argued topic, with benefits often weighed heavily against their potential for being abused outside of a controlled environment. Present uses include: 1 DRUGS OVERVIEW AND HISTORY Cannabis Cocaine GHB Heroin Amphetamines Mushrooms Documented in medicine since the 16th century, it is used restrictively as A naturally occumring substance, its synthesis was first documented in Use dates back Introduced in 1874 Introduced to Modem use has been documented since 1955, with the psychedelic fungi used to affect sensory perception and emotion. to ancient times as an altemative to medicine in 1927 as morphine; now used as a painkiller under its chemical name a decongestant. Today it is used as an aid in childbirth. Today it is used mostly in palliative care. an anesthetic and widely as a psychostimulant drug to increase vasoconstriction 1874, and is now agent. used in the Diamorphine in controlled treatment of focus. narcolepsy. situations. Ancient Times 1400s 1500s 1600s 1700s 1800s 1900s 2000 Opium Methamphetamine LSD Barbiturates Ketamine Ecstasy A core medicinal drug introduced in 1962 for dissocia- tive anesthesia, used most often An FDA approved Used as a painkiller for centuries until its addictive properties First suggested in 1947 for use in Now replaced largely with a safer group of sedatives (Benzodiazepines), the drugs became popular in the 1960s and 1970s as treatment for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Used in the 1970s to treat patients with psychological problems. drug used in treating ADHD and exogenous obesity. First used in Japan in 1893 to alleviate fatigue and produces feelings of alertness. psychiatric treatment and restricted its use. psychotherapy to for sedation in intensive care cause sensory expansion. units. 2 MEDICAL BENEFITS AND CLINICAL USES Safety Classifications: K Cannabis S Barbiturates Drugs in the U.S. are classified under different safety levels. Schedule I drugs are those with a high potential for abuse, and not currently accepted medical use in treatment in the U.S. Schedule II have a high potential for abuse, and Schedule III have a potential for abuse. Schedule I Methamphetamine Heroin Schedule II Ecstasy Mushrooms Schedule III Opium Cocaine A Amphetamines LSD NEUROLOGICAL O GHB Ketamine May Inhibit Tumor Growth PSYCHOTHERAPY Pain and Cluster Headache Relief Treatment of Treatment of Seizures Bipolar Disorder Treatment of Depression Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder OPHTHALMOLOGY & OTOLARYNGOLOGY Treatment of Surface Anesthetic for Mouth/Nose/Throat Insomnia and Anxiety 米 Relieves Intraocular Pressure Treatment in Psychotheraphy, Anxiety and Alcoholism RESPIRATORY Treatment of Narcolepsy Lowers Resistance in the Airway .... .... ABDOMINAL/LIVER V Stimulates MYOCARDIAL Appetite Treatment of Obesity Relieves Heart Attack Pain Increases Heart Rate and Blood Pressure INTESTINAL Treatment of Diarrhea PALLIATIVE CARE Reduces Fibromyalgia Symptoms A Controlled Analgesia, and to Control Nausea and Vomiting associated with Cancer Chemotherapy LABOR PAIN Pain Inhibitor Epidural Anesthesia LOCAL ANESTHETIC Central Nervous System Depressant Used in Emergency and ICU Sedation Decreases Bleeding and Swelling MOVEMENT General Anesthetic K Controls MS Symptoms PHYSICAL TRAUMA Treatment of Neuropathic Pain Alleviates Cachexia and Muscle Waste Relieves Post-Surgical and Chronic Pain Treatment of Cataplexy *Legal use of these drugs in medicine varies between countries. SOURCES: medicinenet.com, emedicine.medscape.com, en.wikipedia.org, nuaa.org.au, nawrot.psych.ndsu.nodak.edu, altmed.creighton.edu, webmd.com, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, cannabismd.net, psychoactive.org.uk, narconon.org, emedicinehealth.com, psychedelic-library.org, healthvermont.gov, cesar.umd.edu, deadiversion.usdoj.gov MEDICAL INFORMATION PROVIDED BY: http://www.medicalbillingandcoding.org/ BILLING & CODING Although these drugs are often thought of negatively because of how often they're abused, they do have several medical benefits that have been utilized and MEDICAL USES OF ABUSED DRUGS analyzed through the years. Read more: The use of these drugs in medicine is a heavily argued topic, with benefits often weighed heavily against their potential for being abused outside of a controlled environment. Present uses include: 1 DRUGS OVERVIEW AND HISTORY Cannabis Cocaine GHB Heroin Amphetamines Mushrooms Documented in medicine since the 16th century, it is used restrictively as A naturally occumring substance, its synthesis was first documented in Use dates back Introduced in 1874 Introduced to Modem use has been documented since 1955, with the psychedelic fungi used to affect sensory perception and emotion. to ancient times as an altemative to medicine in 1927 as morphine; now used as a painkiller under its chemical name a decongestant. Today it is used as an aid in childbirth. Today it is used mostly in palliative care. an anesthetic and widely as a psychostimulant drug to increase vasoconstriction 1874, and is now agent. used in the Diamorphine in controlled treatment of focus. narcolepsy. situations. Ancient Times 1400s 1500s 1600s 1700s 1800s 1900s 2000 Opium Methamphetamine LSD Barbiturates Ketamine Ecstasy A core medicinal drug introduced in 1962 for dissocia- tive anesthesia, used most often An FDA approved Used as a painkiller for centuries until its addictive properties First suggested in 1947 for use in Now replaced largely with a safer group of sedatives (Benzodiazepines), the drugs became popular in the 1960s and 1970s as treatment for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Used in the 1970s to treat patients with psychological problems. drug used in treating ADHD and exogenous obesity. First used in Japan in 1893 to alleviate fatigue and produces feelings of alertness. psychiatric treatment and restricted its use. psychotherapy to for sedation in intensive care cause sensory expansion. units. 2 MEDICAL BENEFITS AND CLINICAL USES Safety Classifications: K Cannabis S Barbiturates Drugs in the U.S. are classified under different safety levels. Schedule I drugs are those with a high potential for abuse, and not currently accepted medical use in treatment in the U.S. Schedule II have a high potential for abuse, and Schedule III have a potential for abuse. Schedule I Methamphetamine Heroin Schedule II Ecstasy Mushrooms Schedule III Opium Cocaine A Amphetamines LSD NEUROLOGICAL O GHB Ketamine May Inhibit Tumor Growth PSYCHOTHERAPY Pain and Cluster Headache Relief Treatment of Treatment of Seizures Bipolar Disorder Treatment of Depression Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder OPHTHALMOLOGY & OTOLARYNGOLOGY Treatment of Surface Anesthetic for Mouth/Nose/Throat Insomnia and Anxiety 米 Relieves Intraocular Pressure Treatment in Psychotheraphy, Anxiety and Alcoholism RESPIRATORY Treatment of Narcolepsy Lowers Resistance in the Airway .... .... ABDOMINAL/LIVER V Stimulates MYOCARDIAL Appetite Treatment of Obesity Relieves Heart Attack Pain Increases Heart Rate and Blood Pressure INTESTINAL Treatment of Diarrhea PALLIATIVE CARE Reduces Fibromyalgia Symptoms A Controlled Analgesia, and to Control Nausea and Vomiting associated with Cancer Chemotherapy LABOR PAIN Pain Inhibitor Epidural Anesthesia LOCAL ANESTHETIC Central Nervous System Depressant Used in Emergency and ICU Sedation Decreases Bleeding and Swelling MOVEMENT General Anesthetic K Controls MS Symptoms PHYSICAL TRAUMA Treatment of Neuropathic Pain Alleviates Cachexia and Muscle Waste Relieves Post-Surgical and Chronic Pain Treatment of Cataplexy *Legal use of these drugs in medicine varies between countries. SOURCES: medicinenet.com, emedicine.medscape.com, en.wikipedia.org, nuaa.org.au, nawrot.psych.ndsu.nodak.edu, altmed.creighton.edu, webmd.com, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, cannabismd.net, psychoactive.org.uk, narconon.org, emedicinehealth.com, psychedelic-library.org, healthvermont.gov, cesar.umd.edu, deadiversion.usdoj.gov MEDICAL INFORMATION PROVIDED BY: http://www.medicalbillingandcoding.org/ BILLING & CODING
Medical Uses Of Abused Drugs
Source
Unknown. Add a sourceCategory
HealthGet a Quote